Difference between revisions of "Finding Camera Stream Paths"
| (52 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This page | This page contains methods and approaches for getting cameras to work with ZM. The best results will be with cameras tested by users in the [[Hardware Compatibility List]]. Next will be with cameras that detail the path in user manuals, and or are Onvif compliant. Proprietary and undocumented cameras are more difficult. | ||
Overall, this can be as simple as looking in the user manual, or as complicated as reverse engineering and breaking into the device. | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Typical methods of obtaining the cameras paths in order of | Typical methods of obtaining the cameras paths in order of easiest to hardest are: | ||
*User Manual/Website | *User Manual/Website | ||
| Line 10: | Line 14: | ||
*Get access to the camera shell | *Get access to the camera shell | ||
*Sniff network packets with TCPDump or Wireshark | *Sniff network packets with TCPDump or Wireshark | ||
*Reverse Engineer | |||
Double check that you don't have any other settings that may block cameras communicating to your computer (firewall, antivirus, etc). For new users who install using the [https://wiki.zoneminder.com/Helpful_user_contributed_resources#Installation_Procedure recommended install] guides, this should not be a concern. | |||
'''Important:''' While doing this testing, you want to keep in mind the following: | |||
* Test outside of ZM, first. (this is faster) | |||
* Verify that ffmpeg / vlc works (see below for examples of usage) | |||
* use the info that works in ffmpeg or vlc in zm. | |||
==Testing out a Camera== | |||
Easy tools to quickly check whether a stream path works in ZM or not are [[VLC]] and [[Ffmpeg]]. | |||
As an example, VLC from the gui (file -> connect to network stream) would connect with a path possibly like | |||
rtsp://<username>:<password>@<ipaddress>:<port>/<somepath> | |||
See the hardware compatibility lists for more details. Port for RTSP is usually but not always 554. | |||
If you want to test from the terminal without X, you can use ffmpeg | |||
$ ffmpeg -i rtsp://<username>:<password>@<ipaddress>:<port>/<somepath> output.mp4 | |||
or (from X) | |||
$ ffplay rtsp://<username>:<password>@<ipaddress>:<port>/<somepath> | |||
If the stream connects, it will provide you with some information about the stream encoding, and also the resolution. | |||
Note that the above are examples for RTSP. You would use http for MJPEG. See the [[Hardware Compatibility List]] for more details. | |||
==Required Fields== | ==Required Fields== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 49: | ||
If you are unsure how to fill in the information into Zoneminder, refer to the [[Hardware Compatibility List]] for other cameras, and copy them. | If you are unsure how to fill in the information into Zoneminder, refer to the [[Hardware Compatibility List]] for other cameras, and copy them. | ||
Note that the results you get from cameras will differ depending on how you connect to the camera (whether you choose, remote, ffmpeg, or libvlc in ZM). | |||
===Example Camera=== | |||
Here's an example of one camera setup in ZM. Note that this is not the only way to setup cameras. There are a lot of other approaches that would've been equally viable. But in this example, we use FFMPEG, motion detection, a preview of 800x600, and h264 passthrough so that recorded videos are the full resolution (1920x1280). Also note that with this camera it's possible to set parameters via the address (e.g. the ? at the end of the URL can have fps or resolution set) which makes it easier to maintain the cameras instead of having to use the Web interface of the camera. | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Zmcamera example1.png|General Tab|link=https://wiki.zoneminder.com/images/a/ae/Zmcamera_example1.png | |||
File:Zmcamera example2.png|Source Tab|link=https://wiki.zoneminder.com/images/5/52/Zmcamera_example2.png | |||
File:Zmcamera example3.png|Storage Tab|link=https://wiki.zoneminder.com/images/f/ff/Zmcamera_example3.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Methods== | ==Methods== | ||
===User Manual=== | ===User Manual=== | ||
Reputable name brand cameras | Reputable name brand cameras will provide video stream paths in the user manual or website. If you bought an unbranded cheap camera or one of the proprietary 'cloud' cameras sold in retail stores then you must move onto the other options. | ||
[[File:Usermanualexample1.png|350px|thumb|right|Here, the user manual indicates the RTSP path.]] | |||
===Onvif=== | ===Onvif=== | ||
Starting with Zoneminder 1.30.4 there is an | Starting with Zoneminder 1.30.4 there is an Onvif probe option in the camera configuration. You can also use external Onvif programs. Onvif is an open standard protocol, where you can get the path information from the cameras, and possibly other information such as PTZ commands or motion detection. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ONVIF | ||
===Web Search Online=== | ===Web Search Online=== | ||
Ispyconnect has a large database of URLs available for cameras. The ZM wiki has some. Use a search engine. You may also come across a telnet or ssh password, which can be used to gain access to the camera | Ispyconnect has a large database of URLs available for cameras. The ZM wiki has some. Use a search engine. You may also come across a telnet or ssh password, which can be used to gain access to the camera shell. | ||
===Camera Shell=== | ===Camera Shell=== | ||
Many cameras run GNU/Linux. If you can get access to the files on the camera, through telnet, or through exploiting a vulnerability in the camera, then you can look around for paths. You may be able to send files from the camera to your local machine using FTP. Cameras often have busybox, or similar utils. Running the command "strings" on binaries may come up with something. Run nmap on the camera to see what ports are open. See more details in external links. | Many cameras run GNU/Linux. If you can get access to the files on the camera, through telnet, or through exploiting a vulnerability in the camera, then you can look around for paths. You may be able to send files from the camera to your local machine using FTP. Cameras often have busybox, or similar utils. Running the command "strings" on binaries may come up with something. Run nmap on the camera to see what ports are open. See more details in external links at the bottom. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ nmap -p1-65535 <ipaddressofcamera> | $ nmap -p1-65535 <ipaddressofcamera> | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Wireshark=== | ===Wireshark/TCPdump=== | ||
Watch the packets coming from the camera when accessing the video stream, and determine where the stream is located if possible. Some cameras require custom authentication, so if your camera is proprietary, then things are more difficult. This is the danger of purchasing cameras that don't follow the standard (onvif). Some cameras will also announce the camera stream URL when they boot on the network. Wireshark and or TCPdump can be useful for this. At the least, they may indicate the IP address. | |||
===Reverse Engineering=== | |||
Reverse engineering is one possibly time-intensive method of getting information from a given camera. See the reverse engineering links below. | |||
==Tips/Troubleshooting== | |||
* Some cameras have limited space for username / password. Be wary of the camera cutting off the end of the password. | |||
* Some cameras don't handle special characters in passwords well. https://forums.zoneminder.com/viewtopic.php?f=40&p=117987#p117987 | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 100: | ||
*[https://www.ispyconnect.com/sources.aspx iSpy Database] | *[https://www.ispyconnect.com/sources.aspx iSpy Database] | ||
*[http://zoneminder.readthedocs.io/en/latest/userguide/definemonitor.html Official ZM Documentation] on this subject | *[http://zoneminder.readthedocs.io/en/latest/userguide/definemonitor.html Official ZM Documentation] on this subject | ||
*[https://shinobi.video/docs/cameras Shinobi List] | *[https://shinobi.video/docs/cameras Shinobi List] | ||
===Reverse Engineering Links=== | |||
*https://web.archive.org/web/20180124024708/https://github.com/sgayou/medfusion-4000-research/blob/master/doc/README.md Advanced reverse engineering/exploitation of a medical device | |||
*https://www.contextis.com/blog/push-hack-reverse-engineering-ip-camera Reverse Engineering an IP Camera | |||
*https://alexhude.github.io/2019/01/24/hacking-leica-m240.html Reverse Engineering a consumer camera | |||
*http://web.archive.org/web/20190609073446/https://hclxing.wordpress.com/2019/05/30/reverse-engineering-wyzesense-bridge-protocol-part-i/ Wyzesensor reverse engineering (1/3) | |||
*http://web.archive.org/web/20190606222131/https://hclxing.wordpress.com/2019/05/30/reverse-engineering-wyzesense-bridge-protocol-part-ii/ Wyzesensor reverse engineering (2/3) | |||
*https://hclxing.wordpress.com/2019/06/06/reverse-engineering-wyzesense-bridge-protocol-part-iii/ Wyzesensor reverse engineering (3/3) | |||
*https://github.com/EliasKotlyar/Xiaomi-Dafang-Hacks Xiaomi / Wyzecam Camera Reverse Engineering | |||
*https://www.eionix.co.in/2019/10/10/reverse-engineer-ddpai-firmware.html Reverse Engineering a Dashcam | |||
*Huang, Andrew "Bunnie", (2017) The Hardware Hacker. pg 279. No Starch Press. | |||
*http://web.archive.org/web/20201102155358/https://wrongbaud.github.io/Holiday-Teardown/ | |||
*http://web.archive.org/web/20210212100444/https://frdmtoplay.com/patching-in-fahrenheit/ - Disassembly and patching. | |||
*https://unnamedre.com/ Podcast on reverse engineering. I haven't listened to it yet, but it may be a valuable reference. | |||
*https://www.eevblog.com/forum/reviews/identifying-the-mcu-from-rt85-handheld-radio/ - firmware hacking of a handheld radio | |||
*http://web.archive.org/web/20230210164816/https://eta.st/2023/01/31/rail-tickets.html - qr codes | |||
*https://github.com/racerxdl/stm32f0-pico-dump | |||
*https://hackaday.com/2022/05/04/dumping-encrypted-at-rest-firmware-of-xiaomi-smart-kettle/ | |||
*https://hackaday.com/2023/02/05/need-to-dump-a-protected-stm32f0x-use-your-pico/ | |||
*https://youtu.be/Y7Z5Q_sNqUw SUPERCON 2022: Kuba Tyszko Cracks Encrypted Software | |||
*https://hackaday.com/2024/01/19/alarm-panel-hack-defeats-encryption-by-ignoring-it/ - Sometimes you can just go right to the display and buttons and ignore the rest of the device | |||
[[Category:Dummies_Guide]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:13, 4 April 2024
This page contains methods and approaches for getting cameras to work with ZM. The best results will be with cameras tested by users in the Hardware Compatibility List. Next will be with cameras that detail the path in user manuals, and or are Onvif compliant. Proprietary and undocumented cameras are more difficult.
Overall, this can be as simple as looking in the user manual, or as complicated as reverse engineering and breaking into the device.
Overview
Typical methods of obtaining the cameras paths in order of easiest to hardest are:
- User Manual/Website
- Onvif probe
- Search online resources and forums
- Get access to the camera shell
- Sniff network packets with TCPDump or Wireshark
- Reverse Engineer
Double check that you don't have any other settings that may block cameras communicating to your computer (firewall, antivirus, etc). For new users who install using the recommended install guides, this should not be a concern.
Important: While doing this testing, you want to keep in mind the following:
- Test outside of ZM, first. (this is faster)
- Verify that ffmpeg / vlc works (see below for examples of usage)
- use the info that works in ffmpeg or vlc in zm.
Testing out a Camera
Easy tools to quickly check whether a stream path works in ZM or not are VLC and Ffmpeg. As an example, VLC from the gui (file -> connect to network stream) would connect with a path possibly like
rtsp://<username>:<password>@<ipaddress>:<port>/<somepath>
See the hardware compatibility lists for more details. Port for RTSP is usually but not always 554.
If you want to test from the terminal without X, you can use ffmpeg
$ ffmpeg -i rtsp://<username>:<password>@<ipaddress>:<port>/<somepath> output.mp4 or (from X) $ ffplay rtsp://<username>:<password>@<ipaddress>:<port>/<somepath>
If the stream connects, it will provide you with some information about the stream encoding, and also the resolution.
Note that the above are examples for RTSP. You would use http for MJPEG. See the Hardware Compatibility List for more details.
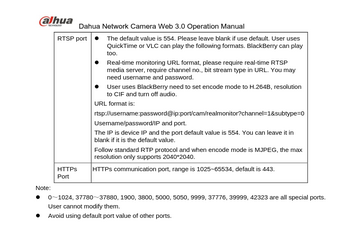
Required Fields
Not all fields are required to be filled in for Zoneminder.
- Resolution must be right.
- Most cameras require username/password.
If you are unsure how to fill in the information into Zoneminder, refer to the Hardware Compatibility List for other cameras, and copy them.
Note that the results you get from cameras will differ depending on how you connect to the camera (whether you choose, remote, ffmpeg, or libvlc in ZM).
Example Camera
Here's an example of one camera setup in ZM. Note that this is not the only way to setup cameras. There are a lot of other approaches that would've been equally viable. But in this example, we use FFMPEG, motion detection, a preview of 800x600, and h264 passthrough so that recorded videos are the full resolution (1920x1280). Also note that with this camera it's possible to set parameters via the address (e.g. the ? at the end of the URL can have fps or resolution set) which makes it easier to maintain the cameras instead of having to use the Web interface of the camera.
Methods
User Manual
Reputable name brand cameras will provide video stream paths in the user manual or website. If you bought an unbranded cheap camera or one of the proprietary 'cloud' cameras sold in retail stores then you must move onto the other options.
Onvif
Starting with Zoneminder 1.30.4 there is an Onvif probe option in the camera configuration. You can also use external Onvif programs. Onvif is an open standard protocol, where you can get the path information from the cameras, and possibly other information such as PTZ commands or motion detection. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ONVIF
Web Search Online
Ispyconnect has a large database of URLs available for cameras. The ZM wiki has some. Use a search engine. You may also come across a telnet or ssh password, which can be used to gain access to the camera shell.
Camera Shell
Many cameras run GNU/Linux. If you can get access to the files on the camera, through telnet, or through exploiting a vulnerability in the camera, then you can look around for paths. You may be able to send files from the camera to your local machine using FTP. Cameras often have busybox, or similar utils. Running the command "strings" on binaries may come up with something. Run nmap on the camera to see what ports are open. See more details in external links at the bottom.
$ nmap -p1-65535 <ipaddressofcamera>
Wireshark/TCPdump
Watch the packets coming from the camera when accessing the video stream, and determine where the stream is located if possible. Some cameras require custom authentication, so if your camera is proprietary, then things are more difficult. This is the danger of purchasing cameras that don't follow the standard (onvif). Some cameras will also announce the camera stream URL when they boot on the network. Wireshark and or TCPdump can be useful for this. At the least, they may indicate the IP address.
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is one possibly time-intensive method of getting information from a given camera. See the reverse engineering links below.
Tips/Troubleshooting
- Some cameras have limited space for username / password. Be wary of the camera cutting off the end of the password.
- Some cameras don't handle special characters in passwords well. https://forums.zoneminder.com/viewtopic.php?f=40&p=117987#p117987
External Links
- iSpy Connect cameras guide
- iSpy Database
- Official ZM Documentation on this subject
- Shinobi List
Reverse Engineering Links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20180124024708/https://github.com/sgayou/medfusion-4000-research/blob/master/doc/README.md Advanced reverse engineering/exploitation of a medical device
- https://www.contextis.com/blog/push-hack-reverse-engineering-ip-camera Reverse Engineering an IP Camera
- https://alexhude.github.io/2019/01/24/hacking-leica-m240.html Reverse Engineering a consumer camera
- http://web.archive.org/web/20190609073446/https://hclxing.wordpress.com/2019/05/30/reverse-engineering-wyzesense-bridge-protocol-part-i/ Wyzesensor reverse engineering (1/3)
- http://web.archive.org/web/20190606222131/https://hclxing.wordpress.com/2019/05/30/reverse-engineering-wyzesense-bridge-protocol-part-ii/ Wyzesensor reverse engineering (2/3)
- https://hclxing.wordpress.com/2019/06/06/reverse-engineering-wyzesense-bridge-protocol-part-iii/ Wyzesensor reverse engineering (3/3)
- https://github.com/EliasKotlyar/Xiaomi-Dafang-Hacks Xiaomi / Wyzecam Camera Reverse Engineering
- https://www.eionix.co.in/2019/10/10/reverse-engineer-ddpai-firmware.html Reverse Engineering a Dashcam
- Huang, Andrew "Bunnie", (2017) The Hardware Hacker. pg 279. No Starch Press.
- http://web.archive.org/web/20201102155358/https://wrongbaud.github.io/Holiday-Teardown/
- http://web.archive.org/web/20210212100444/https://frdmtoplay.com/patching-in-fahrenheit/ - Disassembly and patching.
- https://unnamedre.com/ Podcast on reverse engineering. I haven't listened to it yet, but it may be a valuable reference.
- https://www.eevblog.com/forum/reviews/identifying-the-mcu-from-rt85-handheld-radio/ - firmware hacking of a handheld radio
- http://web.archive.org/web/20230210164816/https://eta.st/2023/01/31/rail-tickets.html - qr codes
- https://github.com/racerxdl/stm32f0-pico-dump
- https://hackaday.com/2022/05/04/dumping-encrypted-at-rest-firmware-of-xiaomi-smart-kettle/
- https://hackaday.com/2023/02/05/need-to-dump-a-protected-stm32f0x-use-your-pico/
- https://youtu.be/Y7Z5Q_sNqUw SUPERCON 2022: Kuba Tyszko Cracks Encrypted Software
- https://hackaday.com/2024/01/19/alarm-panel-hack-defeats-encryption-by-ignoring-it/ - Sometimes you can just go right to the display and buttons and ignore the rest of the device