Difference between revisions of "Ubuntu Install ZoneMinder on Ubuntu Server"
| Line 501: | Line 501: | ||
===Secure Apache using mod_security and mod_evasive Modules=== | ===Secure Apache using mod_security and mod_evasive Modules=== | ||
'''Mod_security''' | '''Mod_security''' | ||
Acts as a firewall for web servers and applications, providing protection against brute force attacks. Install it and then restart Apache. | Acts as a firewall for web servers and applications, providing protection against brute force attacks. Install it and then restart Apache. | ||
Revision as of 06:15, 31 March 2020
LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) vorbereiten
Installation Apache
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get dist-upgrade sudo apt-get install apache2
http://<hostname>/
Firewall einrichten
sudo ufw allow ssh sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw allow https sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw status
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
sudo ufw reload
MySQL installieren
sudo apt-get install mysql-server sudo mysql
mysql> SHOW databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | sys | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> exit
Standardmäßig hat MySQL nur den Benutzer root. Mit diesem Benutzer kann man sich an der Datenbank anmelden, wenn man als root auf dem Linux Betriebssystem den Befehl mysql ausführt. Eine Passworteingabe ist nicht nötig.
Es ist empfehlenswert einen weiteren Benutzer anzulegen, der sich per Passwort verbinden kann. So kann beispielsweise über ein PHP Skript etc. auf die Datenbank zugegriffen werden. Der Benutzer kann folgendermaßen angelegt werden:
sudo mysql -e "CREATE USER 'mysqluser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mysqlpassword';" sudo mysql -e "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'mysqluser'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;" sudo mysql -e "FLUSH PRIVILEGES;" mysql -u mysqluser -p exit
Datenbank Adminbenutzer: mysqluser Kennwort: mysqlpassword
PHP-FPM installieren
sudo apt-get install php-fpm sudo a2enmod proxy_fcgi sudo a2enconf php7.2-fpm sudo systemctl restart apache2 sudo systemctl restart php7.2-fpm.service
Webserver Rechte anpassen
Die Webserver Dateien befinden sich Standardmäßig im Verzeichnis /var/www. Damit die PHP Erweiterung funktioniert, muss die Berechtigung angepasst werden. Der Benutzer sowie Gruppe des Verzeichnisses wird auf www-data geändert.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/
Danach setzen wir für das Verzeichnis das setgit Bit. Dadurch werden neu angelegte Dateien und Verzeichnisse automatisch der Gruppe www-data zugewiesen.
sudo find /var/www -type d -exec chmod g+s {} +
Benutzerzugriffe auf Webseiten-Dateien gewähren
Da wir auf das Verzeichnis /var/www ein setgit Bit gesetzt haben werden alle erstellten Dateien oder Verzeichnisse mit der Berechtigung www-data erstellt. Um nun auch mit einem normalen Benutzer Dateien und Verzeichnisse bearbeiten zu können, ohne die Berechtigung zu verändern wird bindfs benötigt.
sudo apt-get install bindfs
Wir erstellen uns im Homeverzeichnis einen Ordner über diesen wir auf das /var/www Verzeichnis zugreifen können.
mkdir ~/websites
Anschließend erstellen wir uns den passenden fstab Eintrag damit der Zugriff mit den passenden Berechtigungen durchgeführt wird.
Passt euch den folgenden Befehl an euren Benutzer an. In meinem Falls verwende ich den Benutzer myroot.
printf "\n\nbindfs#/var/www/ /home/$USER/websites/ fuse force-user=$USER,force-group=$USER,create-for-user=www-data,create-for-group=www-data,create-with-perms=0770,chgrp-ignore,chown-ignore,chmod-ignore 0 0" | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
Überprüfen ob der Befehl richtig ausgeführt wurde:
sudo cat /etc/fstab
# /etc/fstab: static file system information. # # Use 'blkid' to print the universally unique identifier for a # device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices # that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5). # # <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass> # / was on /dev/ubuntu-vg/ubuntu-lv during curtin installation /dev/disk/by-id/dm-uuid-LVM-biSTbFwePFxtmgpVX68Rwa01ddBXHcAixzw1EBpYcV8kumDeCPxLkQnyNX2hkJ8M / ext4 defaults 0 0 # /boot was on /dev/sda2 during curtin installation /dev/disk/by-uuid/c4c0f1b3-7284-4880-a2bc-11ab15c0a5f3 /boot ext4 defaults 0 0 /swap.img none swap sw 0 0 bindfs#/var/www/ /home/myroot/websites/ fuse force-user=myroot,force-group=myroot,create-for-user=www-data,create-for-group=www-data,create-with-perms=0770,chgrp-ignore,chown-ignore,chmod-ignore 0 0
Anschließend das erstellte Verzeichnis aus dem Home-Folder mounten:
sudo mount /home/$USER/websites
PHP testen
PHP Testseite erstellen:
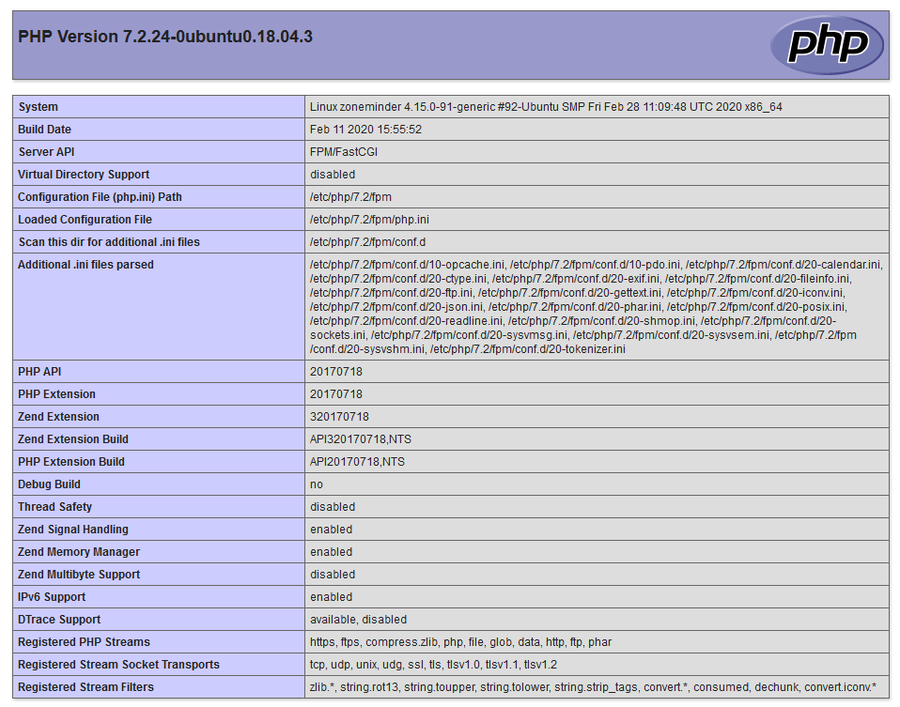
echo "<?php phpinfo();" > ~/websites/html/phpinfo.php
http://<hostname>/phpinfo.php
Installation ZoneMinder
ZoneMinder Repository hinzufügen
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:iconnor/zoneminder-1.34 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
Konfiguration MySQL
sudo rm /etc/mysql/my.cnf sudo cp /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf
sudo vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
[mysqld] # # * Basic Settings # user = mysql pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock port = 3306 basedir = /usr datadir = /var/lib/mysql tmpdir = /tmp lc-messages-dir = /usr/share/mysql skip-external-locking sql_mode = NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
sudo systemctl restart mysql
ZoneMinder Installation
sudo apt-get install zoneminder
Webserver Konfiguration
sudo chmod 740 /etc/zm/zm.conf sudo chown root:www-data /etc/zm/zm.conf sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /usr/share/zoneminder/
sudo a2enmod cgi sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo a2enconf zoneminder sudo a2enmod expires sudo a2enmod headers
sudo vi /etc/php/7.2/fpm/php.ini
[Date] ; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions ; http://php.net/date.timezone date.timezone = "Europe/Berlin"
sudo systemctl restart apache2 sudo systemctl restart php7.2-fpm.service
sudo systemctl enable zoneminder sudo systemctl start zoneminder
Testen ob ZoneMinder funktioniert
http://<hostname>/zm
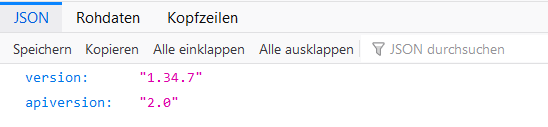
http://<hostname>/zm/api/host/getVersion.json
Konfiguration ZoneMinder
http://<hostname>/zm
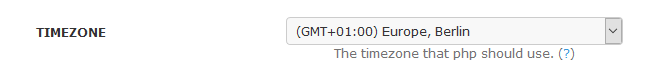
Zeitzone ändern
- Options > System > TIMEZONE >
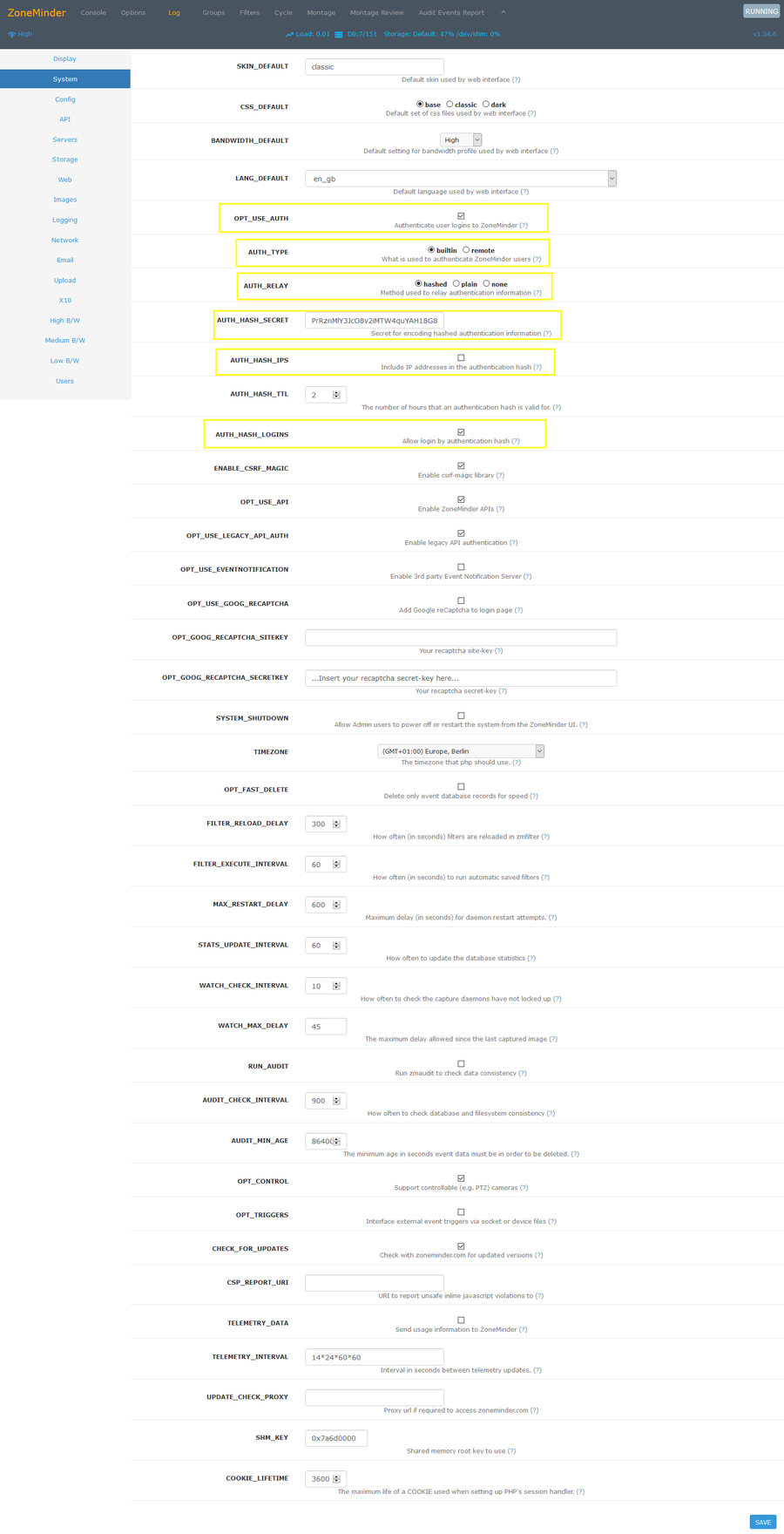
Authentifizierung aktivieren
- Options > System >
- Default Username: admin
- Default Password: admin
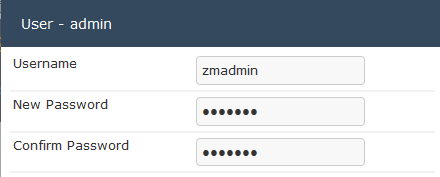
Benutzername und Kennwort ändern
- Options > Users> admin >
- Username: zmadmin
- Password: zmadmin
Datenbank Benutzer und Kennwort ändern
mysql -umysqladmin -p -e "grant lock tables,alter,drop,select,insert,update,delete,create,index,alter routine,create routine, trigger,execute on zm.* to 'zmdbuser'@localhost identified by 'zmdbuser';"
- ZoneMinder Datenbank Benutzername: zmdbuser
- ZoneMinder Datenbank Kennwort: zmdbuser
sudo vi /etc/zm/zm.conf
# ZoneMinder database user ZM_DB_USER=zmdbuser # ZoneMinder database password ZM_DB_PASS=zmdbuser
sudo systemctl restart zoneminder
ZoneMinder NFS Storage
Damit ZoneMinder alle Daten auf einem NFS Share ablegen kann muss dies konfiguriert werden. In meinem Beispiel verwende ich eine Synology als NFS-Server sowie Datenspeicher.
NFS Freigabe erstellen
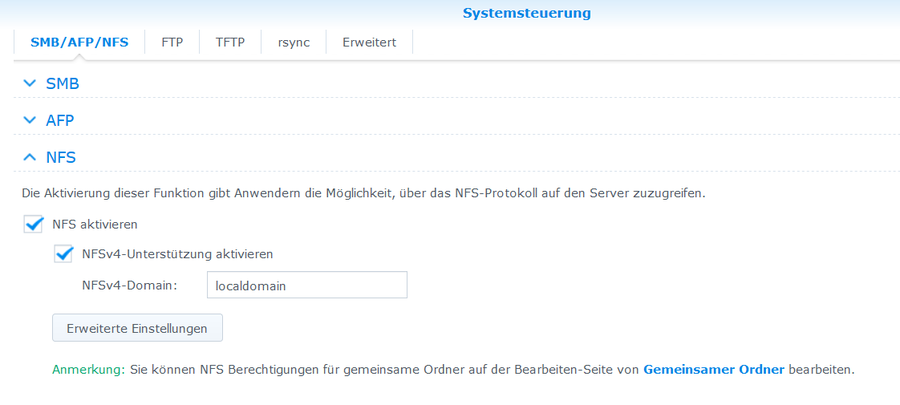
https://<hostname>:5001/
- Systemsteuerung > Dateidienste > NFS >
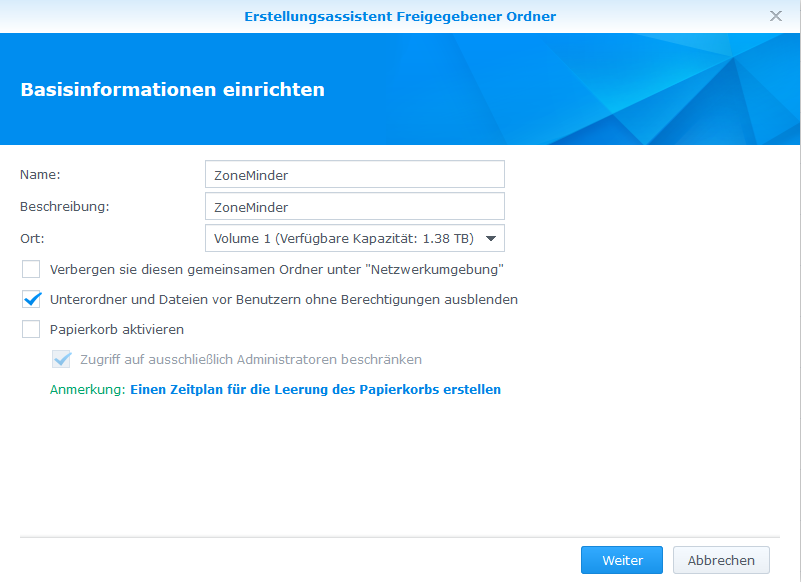
NFS Freigabe Verzeichnis erstellen
- Systemsteuerung > Gemeinsamer Ordner > Erstellen >
NFS Berechtigung setzen
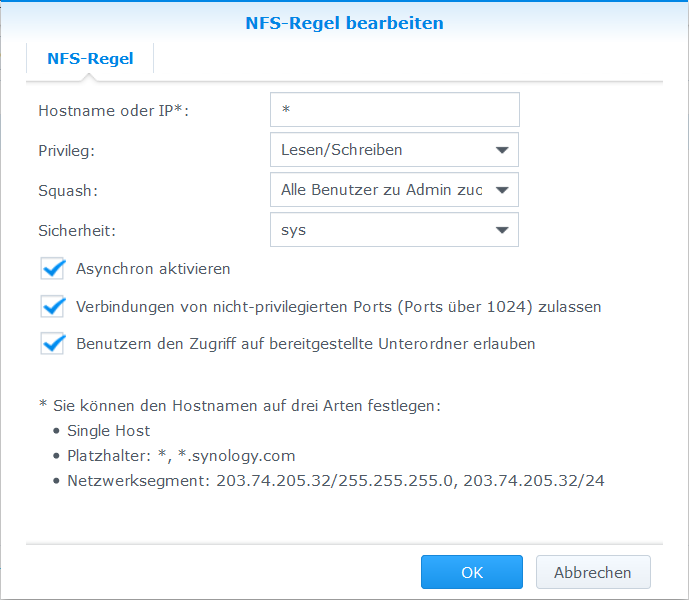
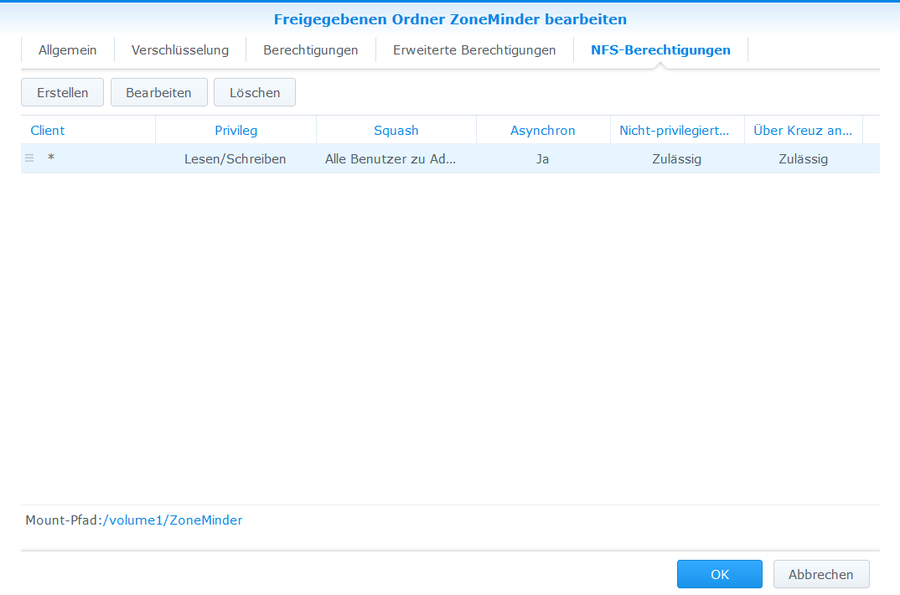
- Systemsteuerung > Gemeinsame Ordner > ZoneMinder > Bearbeiten > NFS-Berechtigungen > Erstellen >
sudo service zoneminder stop
NFS Client installieren und konfigurieren
sudo apt-get install nfs-client nfs-common
sudo modprobe nfs
sudo su - echo NFS | tee -a /etc/modules exit
sudo cat /etc/modules
# /etc/modules: kernel modules to load at boot time. # # This file contains the names of kernel modules that should be loaded # at boot time, one per line. Lines beginning with "#" are ignored. NFS
sudo cp /etc/idmapd.conf /etc/idmapd.conf_orig sudo vi /etc/idmapd.conf
[General] Verbosity = 0 Pipefs-Directory = /run/rpc_pipefs # set your own domain here, if it differs from FQDN minus hostname Domain = localdomain [Mapping] Nobody-User = nobody Nobody-Group = nogroup
ZoneMinder event storage
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/var-cache-zoneminder-events.mount
# systemd NFS mount for ZoneMinder event storage [Unit] Description=NFS mount for ZoneMinder event storage After=network.target Before=zoneminder [Mount] What=192.168.1.5:/volume1/ZoneMinder Where=/var/cache/zoneminder/events Type=nfs [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl enable var-cache-zoneminder-events.mount sudo systemctl start var-cache-zoneminder-events.mount sudo systemctl status var-cache-zoneminder-events.mount
ZoneMinder cache storage
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/var-cache-zoneminder-cache.mount
# systemd NFS mount for ZoneMinder cache storage [Unit] Description=NFS mount for ZoneMinder cache storage After=network.target Before=zoneminder [Mount] What=192.168.1.5:/volume1/ZoneMinder Where=/var/cache/zoneminder/cache Type=nfs [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl enable var-cache-zoneminder-cache.mount sudo systemctl start var-cache-zoneminder-cache.mount sudo systemctl status var-cache-zoneminder-cache.mount
ZoneMinder images storage
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/var-cache-zoneminder-images.mount
# systemd NFS mount for ZoneMinder images storage [Unit] Description=NFS mount for ZoneMinder images storage After=network.target Before=zoneminder [Mount] What=192.168.1.5:/volume1/ZoneMinder Where=/var/cache/zoneminder/images Type=nfs [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl enable var-cache-zoneminder-images.mount sudo systemctl start var-cache-zoneminder-images.mount sudo systemctl status var-cache-zoneminder-images.mount
ZoneMinder temp storage
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/var-cache-zoneminder-temp.mount
# systemd NFS mount for ZoneMinder temp storage [Unit] Description=NFS mount for ZoneMinder temp storage After=network.target Before=zoneminder [Mount] What=192.168.1.5:/volume1/ZoneMinder Where=/var/cache/zoneminder/temp Type=nfs [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl enable var-cache-zoneminder-temp.mount sudo systemctl start var-cache-zoneminder-temp.mount sudo systemctl status var-cache-zoneminder-temp.mount
sudo init 6
Webserver Konfiguration SSL only
SSL Konfiguration
Benötigte Pakete installieren
sudo a2enmod ssl sudo systemctl restart apache2
Self-Signed Zertifikat erstellen
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 3650 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/zoneminder-selfsigned.key -out /etc/ssl/certs/zoneminder-selfsigned.crt
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:DE State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:Hessen Locality Name (eg, city) []:Frankfurt Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:zoneminder.home.lan Email Address []:
sudo chown root:ssl-cert /etc/ssl/private/zoneminder-selfsigned.key
sudo chmod 640 /etc/ssl/private/zoneminder-selfsigned.key
Virtual Host (Port 443) erstellen
sudo a2dissite default-ssl
sudo mv /etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl.conf_orig
sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/zoneminder-ssl.conf
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost _default_:443>
ServerName zoneminder.home.lan
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^/$ https://zoneminder.home.lan/zm/$1 [L,R]
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/zoneminder-error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/zoneminder-access.log combined
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/zoneminder-selfsigned.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/zoneminder-selfsigned.key
<FilesMatch "\.(cgi|shtml|phtml|php)$">
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</FilesMatch>
<Directory /usr/lib/cgi-bin>
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
# vim: syntax=apache ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 sr noet
sudo a2ensite zoneminder-ssl
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Standard Virtual Host (Port 80) deaktivieren
sudo a2dissite 000-default
sudo mv /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf_orig
sudo vi /etc/apache2/ports.conf
# If you just change the port or add more ports here, you will likely also
# have to change the VirtualHost statement in
# /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
#Listen 80
<IfModule ssl_module>
Listen 443
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_gnutls.c>
Listen 443
</IfModule>
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Firewall Port 80 entfernen
sudo ufw delete allow http
sudo ufw status
sudo ufw reload
Hardening Webserver
Hide Apache Version and Operating System
sudo vi /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/security.conf
ServerTokens Prod ServerSignature Off
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Disable Directory Listing and FollowSymLinks
sudo vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
<Directory /var/www/>
Options -Indexes -FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Secure Apache using mod_security and mod_evasive Modules
Mod_security
Acts as a firewall for web servers and applications, providing protection against brute force attacks. Install it and then restart Apache.
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-security2 -y
sudo systemctl restart apache2